A Stable Personalised Partner Selection
for Collaborative Privacy Education
Rita Yusri, Adel Abusitta, Esma Aïmeur
https://doi.org/10.1145/3386392.3397597
While several e-learning platforms for privacy awareness training have been implemented, they are typically based on traditional learning techniques. More specifically, they do not allow students to cooperate and share knowledge in order to achieve mutual benefits and improve learning outcomes. In this paper, we propose a collaborative e-learning platform for privacy education, which can provide a stable personalized partner selection mechanism using game theory. The proposed mechanism guarantees a stable student-student matching according to students’ preferences (behavior and/or knowledge).
The problem
One of the important problems in the collaborative environments is the lack of mechanisms for selecting the optimal partner(s). Usually, the process of selecting a partners is done randomly or by a student directly.Research contribution
- Propose and implement a stable personalized-based partner selection algorithm based on game theory. In particular, we integrate this algorithm into the proposed collaborative e-learning platform for privacy education.
- Integrate the history of partners’ interactions (knowledge and behavior) into the proposed matching algorithm, in order to allow students to improve their selections and learn from their experience, as well as from their colleagues’ experience.
The Stable Partner Selection Algorithm (SPSA)
The Stable Partner Selection Algorithm (SPSA) is based on ‘Game theory‘. More specifically, we adopt the “stable marriage algorithm” (Gale & Shapley) in order to obtain a perfect one-to-one match between the students of two groups (i.e., two classes) to enforce the collaboration among students from different backgrounds.
Notice: S. Shapley awarded the Nobel Prize in Economics for the theory of stable matching in 2012.
The procedures are divided to:
- Knowledge-based Selection
- Hybrid Selection (Knowledge and behavior based)
- Behavioral evaluation
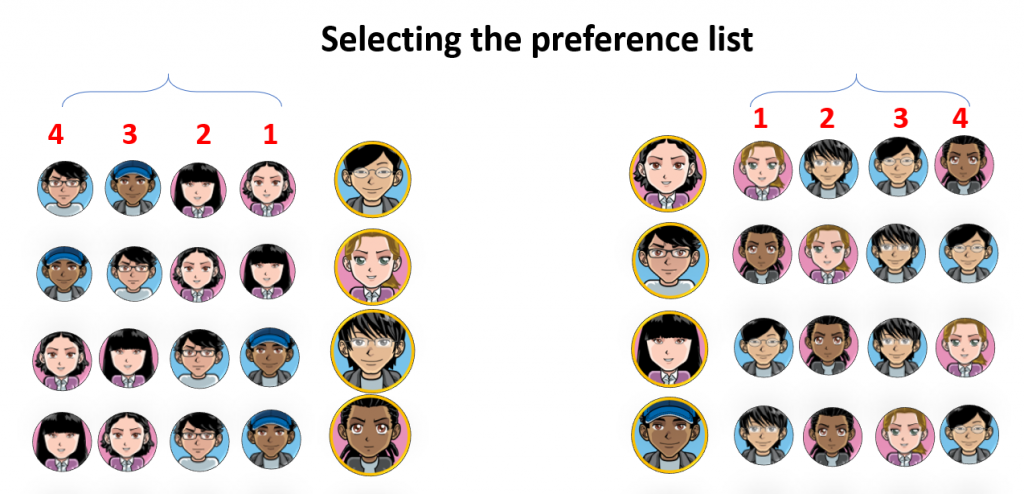
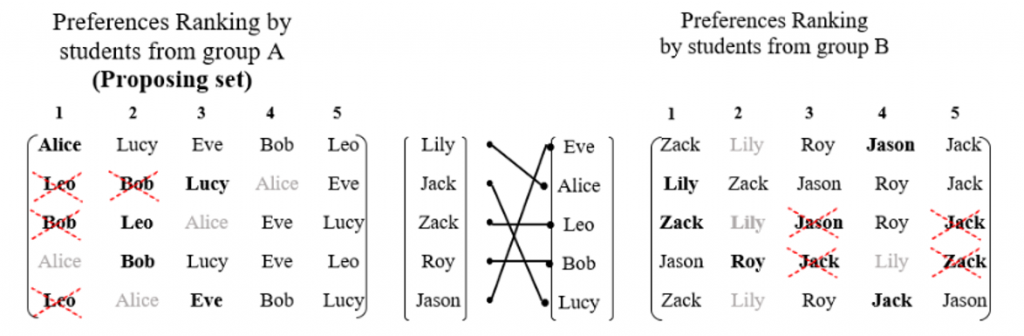
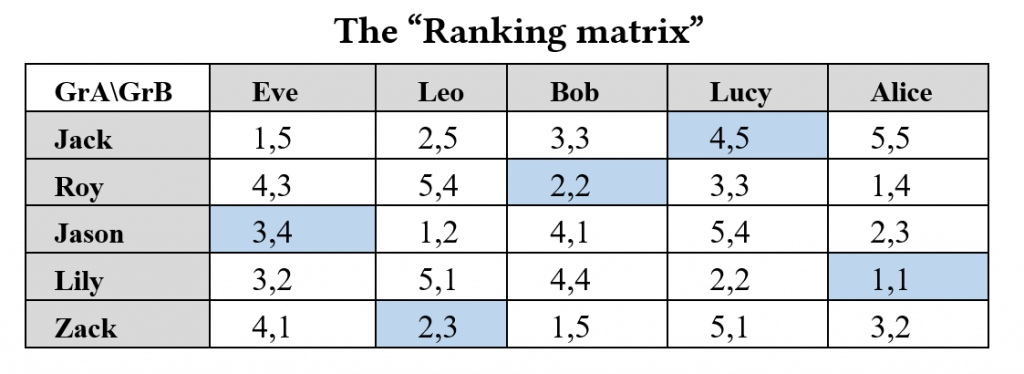 The SPSA algorithm matches students by taking the preference lists as input and producing the stably matched pairs as output.
The SPSA algorithm matches students by taking the preference lists as input and producing the stably matched pairs as output.