Towards Generating Personalized Country Recommendation
Ayoub EL Majjodi, Mehdi Elahi, Nabil El Ioini, Christoph Trattner
With the massive increase in the number of people leaving their country towards a new one for different proposes, either for a good quality of life, increased incomes, or a proper education system. The immigration issue has attracted more attention precisely due to the multidimensional nature of this phenomenon. Often people overwhelmed by the number of information that is circulating on the internet about the best places to live in. Therefore, our work is an attempt to build a personalized country recommender system that assists people to easily find a better place that suits everyone’s needs.
Recommendation Algorithms
To generate country recommendations we adopted the well-known recommender approach, collaborative filtering by using three techniques of this approach:
- k-Nearest Neighbor Algorithm (K-NN)
- Singular Value Decomposition Algorithm (SVD)
- Co-clustering Algorithm
Implementation Details
The user interacts with the system, via a web-based application, designed in such a way that allows users to easily express their preferences and receive suitable recommendations. The figure below illustrates the system architecture.
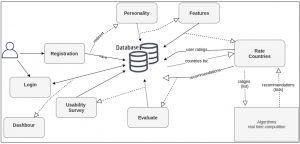
After the features eliciting step in which the user rate some countries (1-5), the system recommended in
 the real-time three lists of countries, each generated by one of the top three recommender algorithms as shown in the figure.
the real-time three lists of countries, each generated by one of the top three recommender algorithms as shown in the figure.
Alongside the list of recommendations the users evaluate the generated recommendation through a questionnaire in terms of various metrics :
- Accuracy
- Diversity
- Understand Me
- User Satisfaction
- Novelty
Experimental setup
The initial dataset of user preferences was collected using a survey in which we were asking people to rate a set of top destination countries of international migrants (IOM 2018). In addition to letting them state a possible reason for immigration.
The survey results :
- 136 respondents
- 3400 ratings for different countries (1-5) scale
The initial dataset was used to cross-validate recommender algorithms in order to select the top preformed ones. Besides, the frequency of the most considered immigration reason was computed, as the table below depicts.

Results
In an offline setup, we cross-validate different recommender algorithms for the purpose of selecting three top algorithms. the cross-validation result illustrated in the table below:

The adopted evaluation metrics for the online assessment of recommender algorithms, yield promising results, they show that there is no winning recommender algorithm in terms of all metrics. The table below shows the comparison of adopted recommender algorithms, based on the opinion of real users.

Conclusion & Future work
- A set of experiments demonstrated the usefulness of recommender algorithms on a complex domain such as immigration.
- As a new direction, explorations of implicit user preferences and adopt more recommender algorithms could enhance the usefulness of the proposed solution.
Paper Link: https://doi.org/10.1145/3386392.3397601
Madness Video : https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=R52ufF5yf7k
